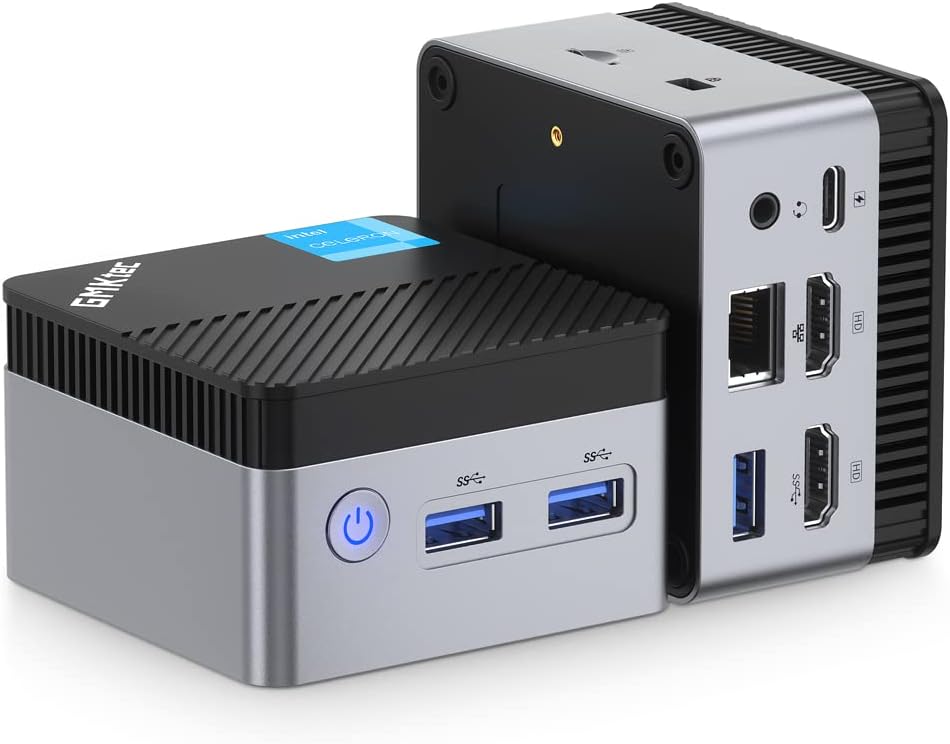

I purchased a miniPC from Aliexpress for about S$130 ( shipping included ). The specification is as follows:
- Intel Celeron N5105 11th Gen 2.0GHz / 2.9GHz (boost)
- 7.2 x 7.2 x 4.4 cm
- 204 grams
- 8GB DDR4 LPDDR4 (soldered on, non expandable)
- 128Gb SATA M.2 2242
- 3x USB-A 3.2
- 2x HDMI 2.0
- 1x Type-C (Power only)
- Gigabit LAN RJ45
- 1x 3.5mm Headphone Jack
- Micro SD Card slot (Max 128GB)
- WIFI 5
- BT 4.2
- Windows 11 Pro
Two interesting aspects is the use of USB C for power and the M.2 slot. The USB C port allows the use of any USB C power adapter (at least 45W) or a power bank that supports at least 22.5W charging. The supplied SSD drive was replaced with a M.2 non SATA drive. The M.2 support a NVME drive that perform a read speed of 1.1 GB/s which is double the SATA speeds.
The fan was not too loud at full load however the CPU temp reached 100C.
One of the reasons I wanted a low end miniPC to test was to see how well it performs for basic tasks like web browsing and video streaming. I deliberately chose the most cost effective Intel based system with adequate performance.
I will installing various Linux distributions and will be testing them. I will report my findings.
 Lets talk about all the ways battery charging is done via cables. Various manufacturers have adopted different methods to
transfer power to the batteries on smartphones and other electronic devices. We will focus on the charging methods used in smartphones.
Lets talk about all the ways battery charging is done via cables. Various manufacturers have adopted different methods to
transfer power to the batteries on smartphones and other electronic devices. We will focus on the charging methods used in smartphones.
One of the product differentiation used by manufacturers is the speed that the phone battery achieve 100% charge. One of the major
standard is the Quick Charge method
Quick Charge
Quick Charge or is also called turbo charging, adaptive fast charging and QC rapid charging. Quick Charge (QC) is a Qualcomm-licensed technology. It’s a marketing phrase that signifies the power managing circuitry capabilities of a wall charger and smartphone. Basically, the technology can charge batteries faster without damaging it. Both the phone, charger and cable must be compatible to enable quick charging.
Although the technology is designed to work with Snapdragon chipsets, Qualcomm had licensed the technology to other vendors chipsets, such as Zenphone (Intel) and Exynos (Samsung).
Rapid charging is applied typically up to the 60-70% range. The charging process will become less aggressive as it reaches the 100% mark. This is to avoid affecting the life span of the battery.
These are three quick charge generations:
QC 1.0 – Devices with QC 1.0 compatibility were first released in 2013. QC 1.0 supports up to 2A and operates on 5V.
QC 2.0 – The next generation of quick charging. QC 2.0 is 50% faster than QC 1.0. It works on a multi-voltage charging system offering 5V, 9V and 12V up to 3A. This multistage voltage means when your device battery is really low it will charge with 12V, this allows for a really rapid charge, then as the charge gets higher it slowly drops the voltage (fixed values) until you reach normal QC 1.0 voltages and speeds.
QC 3.0 – Adds stepless multi-voltage charging, so adapts its voltage to deliver a faster charge. QC 3.0 voltage varies from 3-20V and delivers faster and more economical charging when compared to QC 2.0. QC 3.0 is about 15% faster than QC 2.0
QC 3.0/2.0 chargers can be used to charge older devices with QC 1.0 speeds, ensuring backward compatibility.
USB Power Delivery and Qualcomm Quick Charge 4.0 / 4+
USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) is a standard from USB-IF ( USB Implementers Forum, Inc. ). USB-IF is a non-profit corporation founded by the group of companies that developed the Universal Serial Bus specification. Qualcomm Quick Charge 4+ and USB-PD are intercompatible. USB-PD is used by Apple for their iphones ( iphone 8 and up ). Google Pixel phones also uses USB-PD. Current Samsung high end phones support USB-PD for the highest rate of fast charging.
| Version |
Maximum Power |
Voltage |
Maximum Current |
| USB 2.0 |
2.5 W |
5 V |
500 mA |
| USB 3.1 |
4.5 W |
5 V |
900 mA |
| USB BC 1.2 |
7.5 W |
5 V |
1.5 A |
| USB Type-C 1.2 |
15 W |
5 V |
3 A |
| USB PD |
100 W |
5/9/15/20 V |
5 A |
All USB 2.0 devices provide a minimum of 500 mA at 5 volts. This increases to 900 mA with a USB 3.1 port. USB Type-C ports can be configured in fast charging modes at either 1.5 or 3.0 A for more power when connected to other Type-C devices or chargers. USB-PD is a separate specification that can work across USB 2.0 and 3.0 ports and cables, but you will still need a USB Type-C port due to the communication pins used by the standard.
Power Rules for both USB-PD 2.0 and USB-PD 3.0:
Sources >15W supply 5 volts and 9 volts
Sources >27W supply 5 volts, 9 volts, and 15 volts
Sources >45W supply 5 volts, 9 volts, 15 volts, and 20 volts
Maximum current of 5 A
In order to make use of the highest power modes, specially rated USB cables are required. As standard cables are only rated for 7.5W at most.
The difference between the two types of PD charging (2.0/3.0) lies in the amount of detailed information given by each type of PD. USB-PD 3.0 has worked to improve its power delivery but is primarily known for offering increased amounts of information about the device being charged and its power/ battery.
In addition to faster charging, USB-PD enables both host and peripheral devices to provide power. For example, your phone could be used to charge another device using the same USB-C port.
USB-PD can be used to charge laptops and it is becoming the default fast charging standard.
 eMMC, or embedded multimedia card, is an advanced, managed NAND flash memory for mobile applications and it is still the dominant go-to memory solution for many consumer electronics products. The latest standard is eMMC 5.1. It is can perform either a read or write operation at a time.
eMMC, or embedded multimedia card, is an advanced, managed NAND flash memory for mobile applications and it is still the dominant go-to memory solution for many consumer electronics products. The latest standard is eMMC 5.1. It is can perform either a read or write operation at a time.
UFS is the future of Flash memory. UFS 2.1, the current most pervasive version, offers sequential read/write speeds fast enough to rival SSDs while combining it with the low power consumption of eMMC. At the time of this post, the new UFS 3.0 storage standard is appearing in products like the OnePlus 7 pro and the Samsung Fold. UFS can perform read and write operation at the same time.
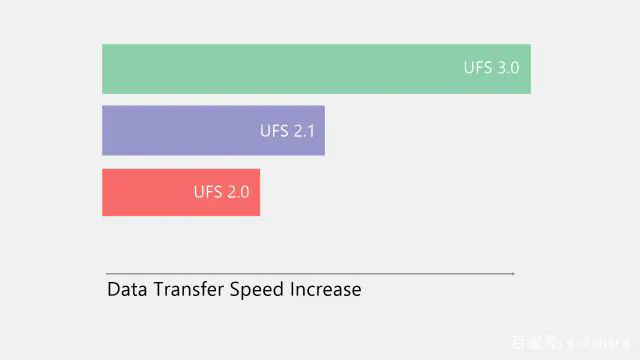
UFS can also process multiple tasks simultaneously while on eMMC user has to wait for one process to complete before they could start another. This makes devices with eMMC slower than UFS based devices when it comes to copying files and booting speed.
What makes UFS 3.0 better than its predecessor is the faster read and write speeds. It is the first standard to offer data transfer speeds of up to 11.6 Gbps simultaneously, which means an overall transfer speed of 23.2Gbps
UFS 2.1 can muster peak speed of 5.9Gbps in one lane, while eMMC can manage speeds of up to 2Gbps only.
eMMC is still popular because of its lower cost. However for premium mobile device lookout for UFS 3.0 storage.

 Lets talk about all the ways battery charging is done via cables. Various manufacturers have adopted different methods to
transfer power to the batteries on smartphones and other electronic devices. We will focus on the charging methods used in smartphones.
Lets talk about all the ways battery charging is done via cables. Various manufacturers have adopted different methods to
transfer power to the batteries on smartphones and other electronic devices. We will focus on the charging methods used in smartphones. eMMC, or embedded multimedia card, is an advanced, managed NAND flash memory for mobile applications and it is still the dominant go-to memory solution for many consumer electronics products. The latest standard is eMMC 5.1. It is can perform either a read or write operation at a time.
eMMC, or embedded multimedia card, is an advanced, managed NAND flash memory for mobile applications and it is still the dominant go-to memory solution for many consumer electronics products. The latest standard is eMMC 5.1. It is can perform either a read or write operation at a time.